A lot of focus is put on generating cleaner energy for a sustainable future, but that’s only one piece of the puzzle. What if we could dramatically reduce our energy consumption just by changing the way we build our office buildings and skyscrapers? Imagine a skyscraper with smart windows and walls made from fungus … yes, a fungus. Let’s explore green building and the future of construction. And can going net-zero really make a difference?
Building homes and skyscrapers with thousands of pounds of concrete, steel, and other materials is a major contributor to pollution and energy use. But it’s more than that. Our homes and office buildings’ lighting, heating and cooling, poor insulation, and integration into the surrounding environment have a lasting impact on energy use and costs. They require larger amounts of power and water to keep comfortable, which just keeps going indefinitely.
Buildings accounted for 28% of energy-related CO2 emissions in 2019.1 In order to reduce that problem, we need some innovations around how we build our houses, offices, and skyscrapers. This is where net-zero and green buildings come in. These constructions are designed and built with the goal of creating positive impacts on the environment and climate. They can combine energy efficiency and renewable energy to reduce power consumption, benefit the environment, and improve quality of life for the people that live or work in those buildings.2 3
The concept of green building has been scaling from small houses to big offices and skyscrapers around the globe. Some international certifications have been developed in order to provide clear guidelines on how to do it.4 The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) developed the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (known as LEED) to rate green buildings and provide owners with a framework of cost-saving, high-efficiency, and health for design, construction, operations, and maintenance.5 Another popular certification is the Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method from the U.K.6. Also known as BREEAM … bree-am? … bream? … who comes up with these acronyms?
Zero-energy buildings have on-site renewable power sources like solar panels to try and produce as much clean energy as it consumes. You can’t always do 100%, but the goal is to get as much as you can. The power generated during the daytime is consumed by the facility, and if there’s an energy surplus, the building delivers it to the grid to try and compensate for grid energy consumption at night. However, to improve efficiency, energy consumption needs to be reduced, so heating, cooling, and lighting needs to be minimized. To achieve that it’s recommended to integrate things like green roofs, energy-efficient windows with triple-pane glass and a low-emissivity coating, as well as good insulation.7 8 Net-zero buildings are also considered “green” if they’re constructed with non-toxic, eco-friendly, and sustainable materials. They should also use less water and have good air quality, so it becomes more sustainable.2 9
Some of the simplest solutions you may have already seen where you work. A good start to make a building more efficient is using high-efficiency LED and smart lighting. Or occupancy sensors that are hooked up to the air conditioning or fan systems. All of those can contribute considerably to reduce energy consumption.10
But taking things to the next level, engineers and architects can perform advanced analysis through 3D building energy simulation tools to achieve higher efficiencies. Some software like Green Building Studio®, Energy Plus, and IES Energy Modeling enable engineers and architects to improve a green building’s design in order to increase their sustainability. They can perform a climate analysis and HVAC simulations, to optimize what materials to use, and how to orient the building for best efficiency. They can see exactly how the building will fare throughout the year before it’s even built.11 12 13 14 15
Examples of green and net-zero buildings have been spreading worldwide over the past decade. In London, for example, Siemens has built The Crystal, one of the greenest buildings in the world. This highly sustainable building is also a unique events venue. It establishes the benchmark for sustainable building design, achieving the Platinum LEED and Outstanding BREEAM accreditation – the most rigorous standards for sustainable design. The Crystal is 70% illuminated by natural light due to its triple glazed windows, and the solar panels produce 20% of the electricity the building uses. Rainwater is collected from the roof and stored in an underground tank for use in the building. 100% of the water used in the toilets is taken from non-potable sources like that. Another interesting feature is the 3,500 data points used by the Siemens Building Management System to monitor the building’s efficiency, which can view water and energy consumption live.16 17 This building cost about £30 million in 2012, but it saves a lot of money with electricity.18 Peter Daw, Cities Projects Developer at Siemens, said “In terms of CO2 savings, we are saving about 71% compared to an equivalent building. In terms of energy costs we are saving about £500,000 a year.” 19
In Seattle, the Bullitt Center is considered one of the greenest commercial buildings in the world. Its structure is mostly composed of heavy timber and the materials were kept to their natural state to avoid the toxins in today’s finishes. And the wood was sourced locally. The triple-glazed curtain wall system, which creates an air tight seal, along with the orientation, provides heat control and improved daytime lighting, so the lights are basically off most of the year. In addition, a closed-loop geothermal system meets the heating and cooling load in the office, and an air-to-air heat exchanger provides incoming fresh air from outside. The Bullitt stores rainwater in a 56,000-gallon cistern in the basement, which is treated and used for non-potable and potable uses20, which means they can use it for drinking water. According to Justin Stenkamp, a mechanical engineer with the company that designed the building’s control and plumbing systems, “These measures alone help to save approximately 80% of water use over a regular office building.”21
At Fully Charged Live at the beginning of 2020 I got a chance to check out the Austin Central Library, which opened in 2017. It’s the first LEEDS Platinum certified building in Austin and is absolutely a gorgeous library. The central atrium isn’t just nice to look at, but it provides daylight to 80% of the occupied spaces. It also has lights that automatically dim depending on how much sunlight is making it into the building, which helps to reduce energy use.
All of that is well and good for building new buildings, but what about existing buildings? One Embankment Place was built in the early 1990s in London for PricewaterhouseCoopers, and it’s a great example of zero-energy retrofitting, and today it’s one of the greenest buildings in the world. It utilizes a tri-generation combined cooling, heat, and power system fueled by recycled waste vegetable oil. It also has several open-plan spaces to harvest day lighting, roof gardens and green walls to make the building more ecological, and low flush toilets to reduce water use. Currently, the One Embankment Place emits 40% less carbon than a typical building of its size; and 20% of its heat and 60% of its energy needs are produced on-site 22 23. From 2007 to 2015, PricewaterhouseCoopers saved £14 million with energy and carbon-related costs.24
Another retrofitting example is the Powerhouse Kjørbo, located in Bærum, Norway. These two office buildings from the 80s were retrofitted with efficient ventilation, insulation, and daylighting. In addition to producing renewable energy on-site, the energy needs of the buildings has been reduced by more than 86%. As a result, Powerhouse Kjørbo received an “outstanding” classification by BREEAM-NOR 25. And probably the coolest part: the building produces about 230,000 kWh but only consumes approximately 100,000 kWh.26
With new buildings and retrofitting old buildings, what’s the forecast for net-zero adoption? According to one report, the global net-zero energy buildings market share was valued at $896.6 million in 2018 and is expected to reach $2.1 billion by 2024 27. That’s some serious growth that’s being spurred on by not only policy, but the value it drives for building owners. Besides reducing utility bills and zeroing out energy use, it can increase the building’s valuation and isolate owners from future energy price variation. On top of that, the benefits also reach people who live or work in green buildings by experiencing fresh air and enjoying an environment more connected to nature 28 29. And there’s the positive impact on the environment due to water conservation, and energy and material efficiency, 30
So, if this is all so great, why is it still a bit unusual to see a green or a net-zero energy office building? I worked in one for years here in Boston, but they’re still hard to come by.
The cost of building a zero-energy building is higher than constructing a common one because the building materials are usually more expensive, and there still isn’t a vast number of designers or builders that are highly skilled and experienced in these types of buildings. Also, high rises have many spaces and occupants in a vertical building with limited roof space for solar panels, so it’s difficult for them to produce all the energy they consume.28 29 31 A study conducted by the United Kingdom Green Building Council (UKGBC) analyzed the feasibility of the design, delivery, and cost of new net-zero-carbon buildings. In the study, they broke it down into two buckets. For offices being built using net-zero goals now through 2025, the cost is about 6.2% higher than standard. Looking further out at newer techniques and standards expected to be the norm by 2030, the cost is 8-17% higher than standard.32
Some governments are rolling out policies to stimulate net-zero, or nearly-zero, energy buildings. The EU’s Energy Performance of Buildings Directive is a good example. It establishes that all new construction must be nearly net-zero from December 31th 2020 — so everything from now onwards needs to meet this criteria. Energy performance certificates must be issued when a construction is rented or sold, and promote smart technologies like building automation and control systems.33
Then there’s the World Green Building Council — a group of 70 Green Building Councils from around the world — who have, among other initiatives, the Net Zero Carbon Buildings Commitment. This challenges organizations, business, cities, states and regions to make all assets under their direct control operate at zero carbon by 2030. There are currently 94 businesses and organizations, 28 cities and 6 States/Regions participating, covering nearly 6,000 assets. By sharing knowledge and lessons learned, the initiative aims to remove barriers to net-zero implementation and inspire others to take action. Oh, and they also have the little goal of making every building in the world decarbonized by 2050.
In addition to green policies, another approach to reduce cost and improve efficiency of net-zero buildings are newer technologies and techniques currently being researched. Such as … fungus. Fungus.
So. Fungus, huh? What about walls made of plant materials? This is still at the experimental stage, but it uses mycelium, a kind of fungal spore that can be used to fill a form with an agricultural product, and the final result is a solid brick or plate. This composite has no toxic chemicals and doesn’t take a lot of energy to make. This material could be used as insulation between non-biodegradable materials to avoid breaking apart since it is biodegradable.34 A project using this material was developed by The Living Studio in New York in cooperation with Ecovative Design. The Hy-Fi Project was a tower about 12 meters high, composed of 10,000 bricks made of mushroom mycelium and shredded corn stalks. When the event ended after three months, the structure was dismantled and the bricks decomposed to compost, exploiting their natural biodegradability.35 While it’s not primarily for net-zero reasons, using mycelium to build structures is being studied by NASA to grow habitats on the Moon and Mars.36 It has higher bend strength than reinforced concrete, is a great insulator, and can regrow and repair itself. If it’s good enough for Martians, why not us?
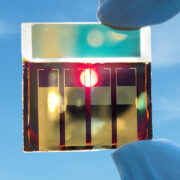
A new technology that deals with solar radiation and its heat is Electrochromic Glass (Smart Glass). It utilizes nanotechnology, which is something I covered in a recent video, to produce small electrical signals to slightly charge the windows in order to change the quantity of radiation they reflect. This tech could help to control the heat inside a building, which could save a lot of money on HVAC costs, mainly in summer.34 37 Usually, smart windows start a blueish color and, after a few minutes, turn transparent when you apply an electrical charge.38 Some companies have been producing and improving this technology. For example, View Inc., an American smart window company implemented a project for Netflix’s office in Los Gatos, CA, that used 56,200 sq. ft. of their smart glass, which uses a predictive, automated system that can be customized and controlled through an app. It takes a holistic view of the building, like the arc of the sun or obstructions to dynamically adjust the tint of the windows.39
As you can see there are a lot of different options and techniques out there for improving how we build our buildings and use energy to keep them comfortable. Even though the costs are still not universally affordable for all office and skyscraper owners, the development of new materials, technologies, design improvements, and government incentives can help the growth of this market worldwide. It’s pretty easy to imagine high-rise buildings and office parks with green roofs and zero energy popping up in more and more cities in the next few decades. Much like Apple Park, which is the largest LEED Platinum certified building.
Jump into the comments and let me know what you think … and if you work or know of net zero buildings in your area. If you liked this video be sure to check out one of the ones I have linked right here. Be sure to subscribe and hit the notification bell if you think I’ve earned it. And as always, thanks all of my patrons and to all of you for watching. I’ll see you in the next one.
- 2019 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction Sector ↩︎
- Zero Energy Buildings ↩︎
- What is green building? ↩︎
- Green building certification systems ↩︎
- What is LEED? ↩︎
- BREEAM ↩︎
- A Common Definition for Zero Energy Buildings ↩︎
- Design Process for a Net-Zero Energy Building ↩︎
- Green Buildings Could Save Our Cities ↩︎
- Advancing Net Zero in High-rise, High-density Asian Cities: Possibility or a Pipe Dream? ↩︎
- 11 ↩︎
- Advancing Net-Zero Energy Commercial Buildings ↩︎
- Autodesk Green Building Studio ↩︎
- Building Energy Modeling with IESVE ↩︎
- EnergyPlus ↩︎
- One of the World’s Most Sustainable Buildings ↩︎
- 10 Coolest Examples of “Green Buildings” ↩︎
- The Crystal ↩︎
- Crystal clean energy efficiency ↩︎
- Bullitt Center ↩︎
- The Bullitt Center Shoots for Net-Zero Water ↩︎
- Price Waterhouse Coopers LLP, One Embankment Place, London ↩︎
- PwC creates the most sustainable building in the world ↩︎
- PwC almost halves energy consumption since 2007 ↩︎
- Powerhouse Kjørbo ↩︎
- Powerhouse Kjørbo ↩︎
- Net Zero Energy Buildings Market is Predicted to Hit Valuation of $2,106.6 Million by 2024: P&S Intelligence ↩︎
- Zero Energy Building ↩︎
- Energy-Efficient Building: Investing Pros, Cons ↩︎
- Eco-friendly Construction: 8 Advantages of Green Building ↩︎
- Pros and Cons of a Net-Zero-Energy Building ↩︎
- Building the Case for Net Zero ↩︎
- Energy Performance of Buildings Directive ↩︎
- Top 10 Green Advances in Commercial Building ↩︎
- Hy-Fi ↩︎
- NASA – Could Future Homes on the Moon and Mars Be Made of Fungi? ↩︎
- The Rise of Green Technology in Construction ↩︎
- “Smart” windows (electrochromic glass) ↩︎
- Project – Netflix ↩︎
- 11 ↩︎















Comments